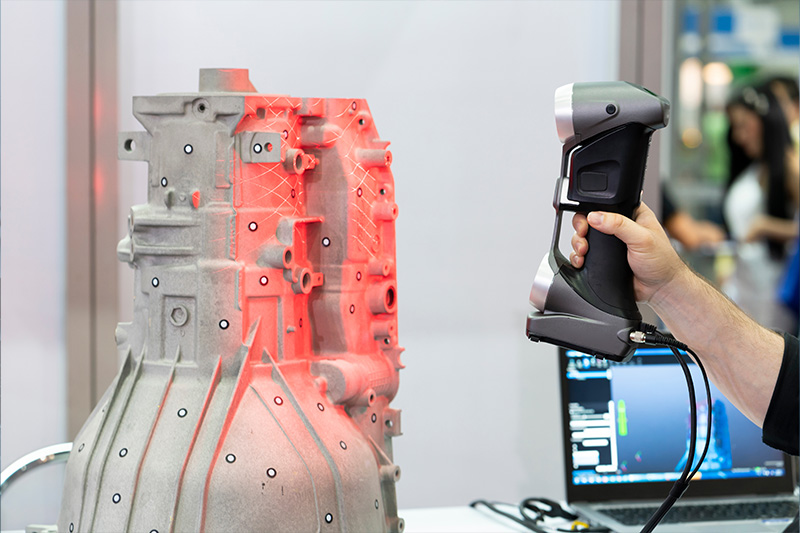
What is 3D Scanning and How Does It Work?
3D scanning is a process of creating a digital 3D model of a real-world object. This is achieved by capturing data points from the object’s surface and then using software to reconstruct a virtual representation. Imagine taking thousands of photographs of an object from every angle and then stitching them together to create a complete 3D model. This is essentially what 3D scanning does.
Benefits and Applications of 3D Scanning
3D scanning has a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most common benefits and applications include:
- Reverse engineering: Creating digital models of existing physical objects for analysis, modification, or reproduction.
- Prototyping: Quickly creating physical prototypes based on digital 3D models.
- Quality control: Inspecting products for defects or deviations from design specifications.
- Medical applications: Creating accurate 3D models of human anatomy for surgical planning, prosthetics, and orthodontics.
- Entertainment: Creating digital characters, props, and sets for movies, video games, and animation.
- Heritage preservation: Digitally preserving historical artifacts and objects.
Types of 3D Scanning Technologies
There are several different types of 3D scanning technologies, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
- Structured light scanning: Projects a pattern of light onto the object and analyzes the distortion of the pattern to create a depth map.
- Time-of-flight scanning: Measures the time it takes for a laser beam to travel to the object and back to calculate distance.
- Laser scanning: Uses a laser to measure the distance between the scanner and the object’s surface.
Basic Steps in the 3D Scanning Process
The 3D scanning process typically involves the following steps:
- Preparing the object: Ensure the object is clean, well-lit, and free of obstructions.
- Scanning the object: Use a 3D scanner to capture data points from the object’s surface.
- Post-processing the scan: Clean up the scan data, remove noise, and align multiple scans if necessary.
Getting Started with 3D Scanning
If you’re interested in getting started with 3D scanning, there are a few things to consider:
- Choosing a 3D scanner: Consider your budget, the type of objects you want to scan, and the desired level of accuracy when selecting a scanner.
- Learning 3D scanning software: There are various software options available for processing and editing scan data.
- Experimentation: Practice with different objects and scanning techniques to improve your skills.
